The Hubble Space Telescope has made some unbelievable discoveries since its launch in 1990 and opened new ways for the astronomers. But science is a field which needs developments and inventions. So, does it mean that the American space agency will replace its current space telescope and is the reason behind its recent engagement with another project?
New favourite telescope
NASA has signed quite a few observations with the Hubble House Telescope but now the space agency is slowly pushing Hubble to the second place. The brand new telescope is known as 100 Hubble WFIRST Telescope which may replace Hubble. The WFIRST, introduced in 2016 can have 100 occasions the viewing angle of the Hubble House Telescope.
Earlier in a press release for NASA stated, "The Wide-Field Instrument will give the telescope the ability to capture a single image with the depth and quality of Hubble, but covering 100 times the area. The coronagraph will provide revolutionary science, capturing the faint, but direct images of distant gaseous worlds and super-Earths."
Facts about WFIRST
This telescope can find stars which can't be noticed as a result of being dimmer in response to the Solar System. The Coronagraph, also known as "star glasses," contains sensors, versatile mirrors, prisms and guards to filter the rays. Since the design won't block the dim stars, these facts can be the strongest weapon of the WFIRST Telescope in observations.
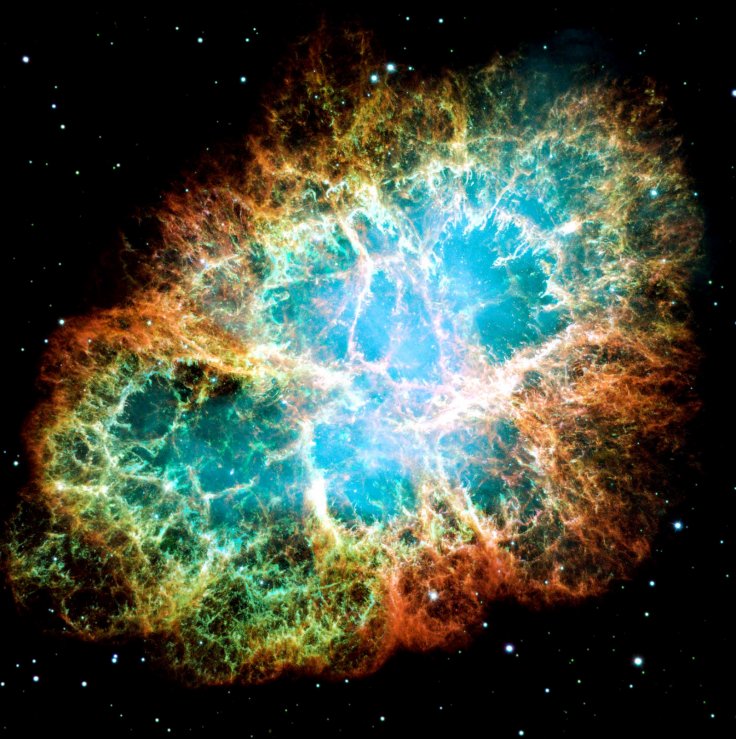
Hubble Space Telescope discoveries
There are 10 thought-provoking discoveries which serve to highlight some of Hubble's greatest scientific achievements to date.
- Discovering a Runaway Universe

Recognizing Worlds Beyond earth
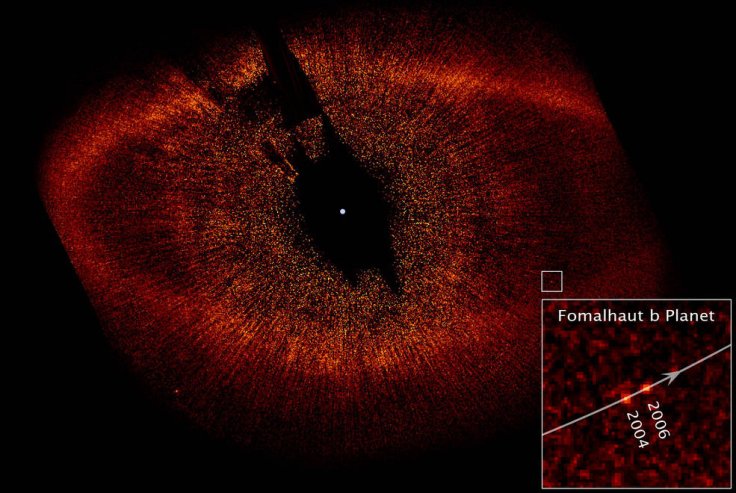
- Shining a Light on Dark Matter
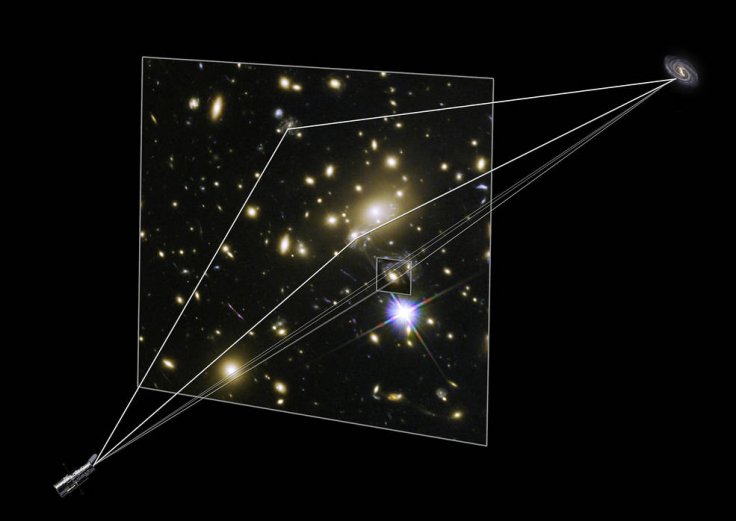
Large galaxy clusters contain both dark matter and normal matter. The immense gravity of all this material warps the space around the cluster, causing the light from objects located behind the cluster to be distorted and magnified. This phenomenon is called gravitational lensing. This sketch shows paths of light from a distant galaxy that is being gravitationally lensed by a foreground cluster. NASA & ESA - Realizing Monster Black Holes Are Everywhere
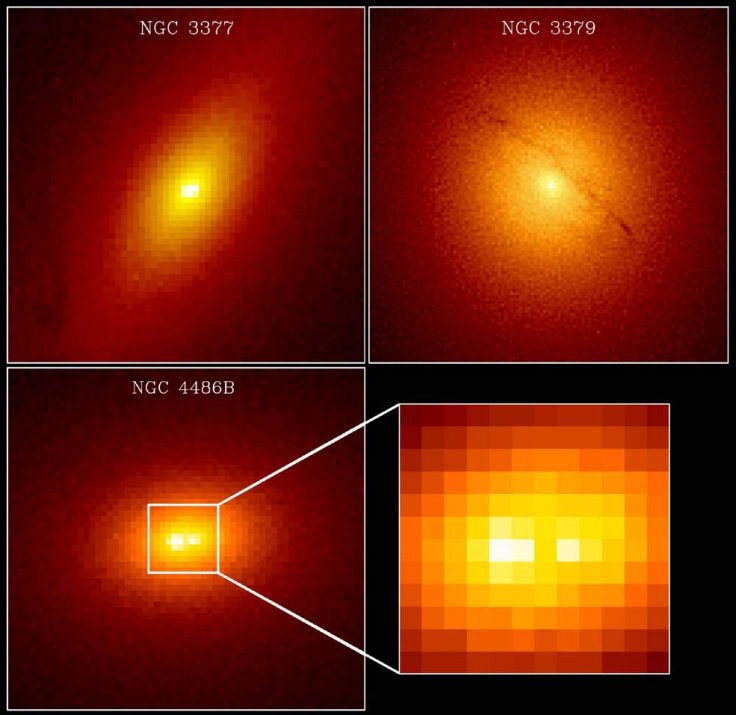
Combining images with data from Hubble’s spectrographs, researchers have peered into the center of many galaxies and established the existence of large black holes. These massive black holes surround themselves with luminous stars and gas, which are visible as bright knots. In a census performed by Hubble in the late 1990s, galaxies NGC 3379 and NGC 3377 were found to have black holes that “weighed in” at 50 million and over 100 million solar masses, respectively, and NGC 4486B was revealed to have a double nucleus at its core. Karl Gebhardt University of Michigan), Tod Lauer (NOAO and NASA - Death Throes of Stars










