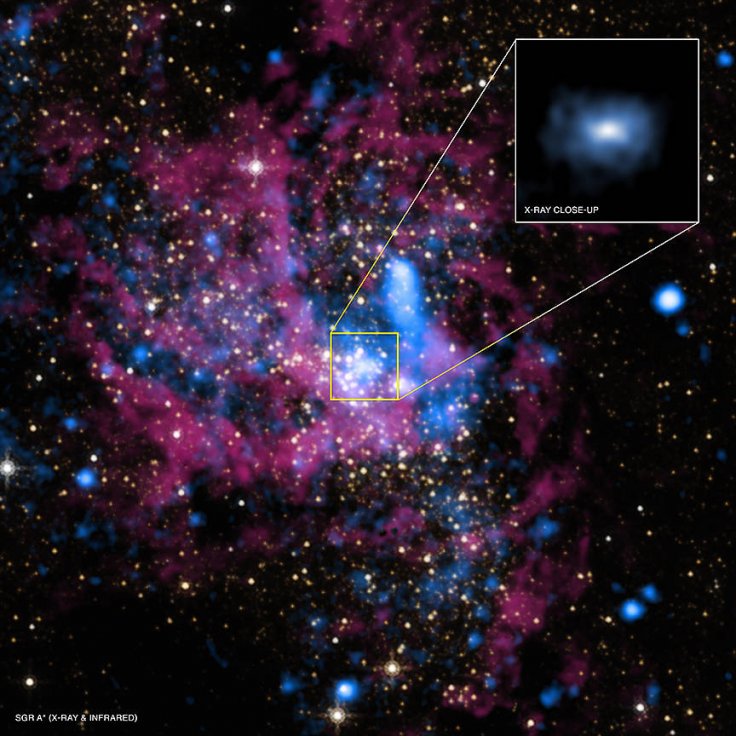
An expert on astrophysics explained how approaching a black hole can cause time to stop and stand still. For her explanation, the astrophysicist used the Milky Way's supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* as an example.
In the field of physics, space-time refers to a model where space and time are intertwined. It can be stretched and affected by various factors such as the gravitational force of an object with great mass.
Black holes and space-Time
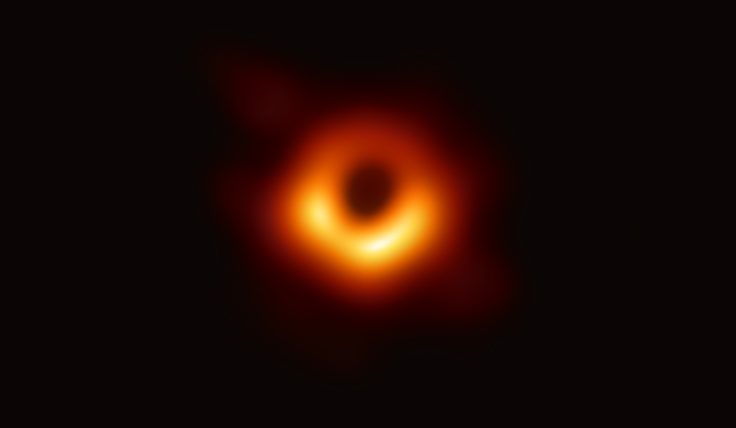
Since black holes are known for their mass and powerful gravitational pull, it is widely believed that these cosmic objects can affect space-time. This means traveling to the center of a black hole could theoretically cause time to stop moving. This subject was discussed by Emma Osbourne, an astrophysicist from the University of Southampton, during a previous New Scientist Live event. During a panel discussion, Osbourne explained how supermassive black holes can stretch space-time.
"If you were to stand just outside the event horizon of Sagittarius A*, and you stood there for one minute, 700 years would pass because time passes so much slower in the gravitational field there than it does on Earth," she said during the event, according to the Express.

Effect of black holes on falling objects
According to Osbourne, the more mass an object has, the more capable it is of stretching space-time due to the gravitational force it can exert. In the Milky Way, Sagittarius A* is one of the densest objects in the galaxy, with a mass that is over four million times that of the Sun. "Anything mass will stretch space-time. And the heavier something is, or the more mass it has, the more it will stretch space-time," Osbourne explained.
Unfortunately, even though black holes are capable of stretching space-time, a person falling into one will probably not be able to witness this effect. This is because as objects approach black holes, they immediately become subjected to their powerful gravitational pull. As other scientists previously explained, falling into a black hole would cause the human body to undergo an excruciating process known as spaghettification. This means the body will be stretched to a point that it becomes a stream of matter falling into the black hole's center.









