Malaysia was one of the countries which seemed to have brought the Coronavirus pandemic under control with daily new cases dropping rapidly. But the numbers are slowly rising once again. Amid the concerns, the Institute of Medical Research (IMR) has found traces of D614G mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
Malaysia's Director-General of Health, Dr Noor Hisham Abdullah clarified that the mutated strain was found in three samples in Sivagangga and one from the Ulu Tiram cluster. In a Facebook post, Hisham said that D614G mutation was first detected in July and the existing vaccine would be ineffective against it.
"It was found to be 10 times likely to infect other individuals and easier to spread by super spreader individuals. So far, these two clusters are under control due to various public health controls in the field," he said.
Hisham also added that people must stay vigilant and must take preventive measures. "The public must stay vigilant and careful as Covid-19 with the D614G mutation has been detected in Malaysia. Continue to take preventive measures and adhere to the standard operating procedures as stipulated, such as physical distancing, self-hygiene practices, and wear a mask when in public places," he said.
What Is D614G Mutation?
When there is a permanent change in the DNA sequence, it is called a mutation. All living organisms mutate to survive. The change or mutation happens due to environmental factors and errors in the replication process. Mutation can be of different types including insertion, deletion, missense, frameshift and repeat expansion among others.
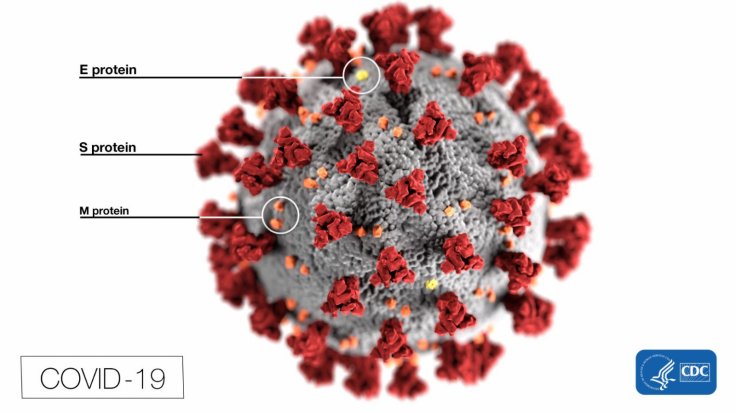
D614G is a missense mutation of the spike protein in which a nucleotide change leads to a codon (sequence of three DNA or RNA nucleotides) that causes differences in amino acid. Although a study found that the mutation increases infectivity, but it isn't as deadly as thought. The mutation was first found in Europe in the early days of the spread and it increased the severity of the COVID-19 disease.
Impact on Vaccine Development
The spike protein is the most talked about in vaccine development as it is located on the surface of the virus that uses it to latch on to the host cells. Initially, there were concerns that the mutation would render existing vaccine development ineffective. Researchers from IMB Cambridge Scientific Center said in their study that the G614 variant could cause antigen drift.
"The highly prevalent G614 variant in the European population may cause antigenic drift, resulting in vaccine mismatches that offer little protection to that group of patients," the study said.
However, it is not likely to affect vaccine development. The D614G mutation although alters the spike protein, making it easy to bind with host cells, it does not change the receptor (ACE2) binding process. Most of the vaccines that are in development are targeted towards the receptor-binding domain to induce an immune response. Thus, the mutation is unlikely to cause any disruption in vaccine development.
"An amino acid change (D614G) outside the RBD was found to be more infectious, but no evidence of being resistant to neutralizing antibodies has been demonstrated," a study by Chinese scientists claimed.









