As many researchers are unclear about the time period of Coronavirus antibodies in recovered patients, Chinese scientists in a new study revealed that the signs of immunity vanish quickly from severe COVID-19 patients in less than a month after being discharged from the hospital. They found that the antibodies drop off sharply once a patient is completely recovered.
As per the study, most of the patients who were sent home from the hospital did show signs of antibodies, which is a sign that their bodies have learned to protect themselves from the virus, but those antibodies were not strong enough to fight Covid-19 for long. To determine the duration of antibody responses, the neutralization activities as well as anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses after hospital discharge were analyzed.
The Chinese study found that around 81 percent of patients had the antibodies but only a "small portion" of those people had any with the ability to neutralize or kill the virus. So, if the body cannot retain antibodies over the long-term, it could suggest that a Coronavirus vaccine may not offer permanent protection, which researchers and vaccine developers are hoping for.
Chinese Study
Researchers from Nanjing University Medical School in China looked at 19 non-severe and seven severe COVID-19 patients for a month. They also observed their antibody response for three weeks. The researchers noticed that the patients had a varying level of antibody response and a small portion of patients are developing a potent level of neutralization activity but did not disclose the actual number.
The study, which was published in PLOS Pathogens, suggests that between three to four weeks after the discharge from the hospital, the neutralizing activity of antibodies from recovered patients has declined significantly. As the world is facing an unprecedented challenge with communities and economies affected by the Coronavirus pandemic, "the development of antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, started to be reported but remained largely elusive," they wrote.
The authors also added that "understanding the adaptive responses where the body makes antibodies that specifically bind to the Sars-CoV-2 among COVID-19 patients provides fundamental information for developing effective treatment and preventive vaccine."

The Confusion
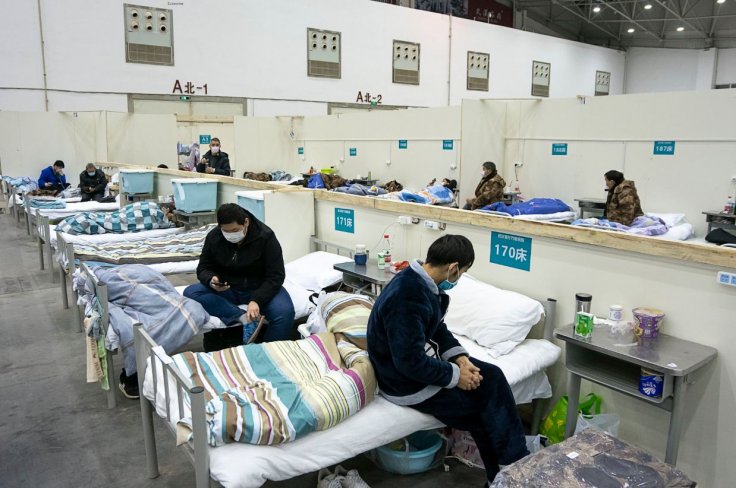
But as per previous studies and other experts, the antibodies can last for months after someone falls sick with the disease. There is also some debate among the researchers about whether the severity of illness plays a role to determine the time period of antibodies.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on its website earlier in an update said that a person who has recovered from the Coronavirus caused disease COVID-19 will likely be safe from reinfection for three months. But the new Chinese study has claimed something opposite.
A professor of immunology at Imperial College London, Danny Altmann, who is also the spokesperson from British Society for Immunology, said this new research paper "makes a number of points: the gold-standard in assessing the antibody response to a virus is measuring the ability to neutralize the entry of the virus into cells."
"We don't know to what extent this is bad news unless we know the extent to which the white blood cells that make the antibody (B cells) are up and ready to defend against any repeat attack," Prof Altmann added.









