With the COVID-19 pandemic continuing rage across the globe, the rush for a potential cure is intensifying. Several potential drugs and treatments are being examined as therapeutic options. Now, researchers have discovered that a naturally occurring enzyme, may serve as a potential low-cost drug to treat the novel coronavirus infection.
According to the study by scientists from the University of California - Los Angeles (ULCA) and a group of Chinese institutions, Catalase, an antioxidant enzyme, was found to neutralize the multiplication of SARS-CoV-2 virus in the body and alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Highlighting that the current focus is on antiviral drugs and vaccines, Yunfeng Lu, senior author of the study, said in a statement, "In the meantime, our research suggests this enzyme could offer a very effective therapeutic solution for treatment of hyperinflammation that occurs due to SARS-CoV-2 virus, as well as hyperinflammation generally."
Easily Available Antioxidant
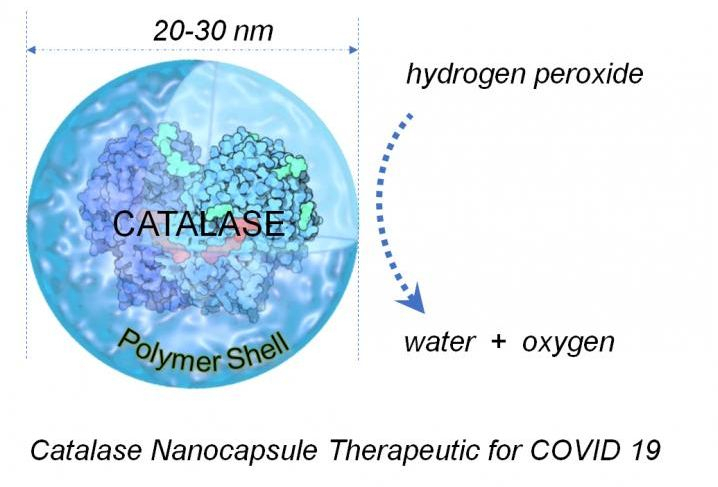
Catalase is a common enzyme that is found in almost all living organisms. It is naturally produced and utilized by plants, humans and animals. It is an antioxidant (i.e) it mitigates the process of oxidation that leads to the release of free radicals, and ultimately cell damage.
The antioxidant triggers the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, which is toxic, into oxygen and water. Catalase is also commonly included in food production worldwide and made use of as a dietary supplement.
Studying the Effects of the Enzyme
For the study, the scientists designed the drug-delivery technology required for the experiments. Then, they conducted three types of tests, each of which addressed a different symptom of the disease.
First, the team demonstrated that the enzyme had anti-inflammatory effects and its capacity to regulate the production of cytokines, a signaling protein produced by lymphocytes or white blood cells. They moderate the immune system by guiding immune cells to the site of infection. However, in the case of severe COVID-19, this mechanism becomes erratic and causes damage to healthy cells. This is known as a "Cytokine Storm".
Proof of Effectiveness Against COVID-19
Next, the team validated that catalase had the ability to protect alveolar cells which line the lungs of human beings from damage on account of oxidation. Finally, they showed that the antioxidant enzyme can suppress the replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in rhesus macaques—a species of monkeys—without any significant toxicity.
This work has far-reaching implications beyond the treatment of COVID-19. Cytokine storm is a lethal condition that can complicate other infections, such as influenza, as well as non-infectious conditions, like autoimmune disease," concluded Dr. Gregory Fishbein, co-author of the study.









