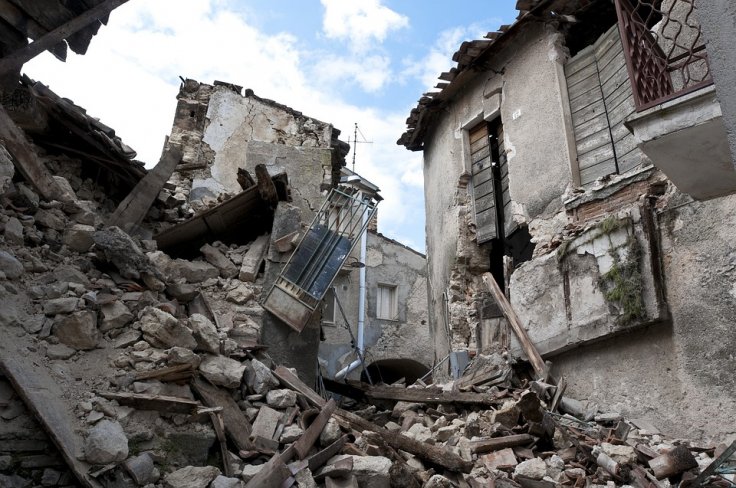
There are fears that Monday's earthquake in Turkey and Syria would go down as the most destructive in the region's modern history. Current estimates are that at least 5,000 people have died and tens of thousands have been injured.
World Health Organisation authorities fear that the actual death toll could rise at least eight times this number. If it does happen, the death toll from the latest earthquake would be higher than the 33,000 people killed when a massive quake hit Turkey's eastern Erzincan province in 1939.
Why are Some Countries More Prone to Quakes?
Earthquakes are a natural phenomenon that can be catastrophic and devastating when tectonic plates slip or shift away. Tremors and shakes are felt when fault lines along the edge of tectonic plates release energy from the Earth's hot molten center.
Scientists say that aftershocks can continue for weeks and months or even years, depending on the size of the mainshock. According to the USGS, the plate boundaries are made up of many faults, and most of the earthquakes around the world occur on these faults. When the plate has moved far enough, the edges unstuck on one of the faults and there is an earthquake.

Why Does the Earth Shake During an Earthquake?
When the edges of the faults are stuck together and the rest of the block is moving, energy is being stored up. The stored up energy gets released when the force of the moving blocks finally overcomes the friction of the jagged edges of the fault and it unsticks. As such, energy radiates outward from the fault in all directions in the form of seismic waves, similar to ripples on a pond. The seismic waves, as per USGS, shake the Earth as they move through it. The ground shakes when the waves reach the Earth's surface.
Countries Prone to Earthquake-driven Death and Destruction
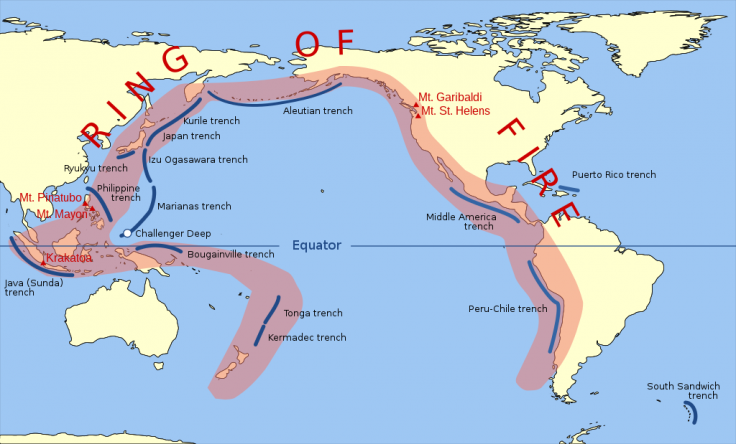
Scientists believe 15 countries around the world account for most of the death and destruction wrought by earthquakes. John Schneider, the Secretary General of the Global Earthquake Model Foundation (GEM), highlighted that GEM scientists factored their study to ground-shake potential, types of buildings, population density, potential for fatalities and economic loss:
- China – Schneider pointed out that China has recorded half the deaths whether the earthquake is over the last 50 years or the last 500 years. The country's huge population of more than 1.3 billion people makes it vulnerable to loss of life and property. China's 1976 earthquake of 7.5-magnitude killed 242,769 people.
- Japan – This Asian island nation is located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, which is the most active earthquake zone on Earth. A 7.9 magnitude earthquake in 1923 in Tokyo killed 142,807 people.
- Iran - Seismologist Frederik Tilmann, from the GeoForschungsZentrum, said Iran is high-risk area for earthquakes as several tectonic plates lie below the country. He explained that the high death rates due to earthquakes is attributed to the rural loam construction method.
- Philippines – This country is also located on the Pacific Ring of Fire.
- Indonesia – Located on the Pacific Ring of Fire, earthquakes are common here.
- Turkey – Earthquakes are common in Turkey as the country is situated on the Anatolian Plate, which borders two major fault lines – the North Anatolian fault and the East Anatolian fault.
- India – like its neighbor China, India is vulnerable to earthquakes because of its huge population and dense cities.
- Mexico – It lies on one of the world's most seismological active regions called the Ring of Fire. An 8.1-magnitude earthquake in 1985 killed more than 10,000 people and destroyed hundreds of buildings.
- Nepal – This Himalayan nation is prone to earthquakes as it sits on two massive tectonic plates, the Indo-Australian and Asian plates. The earthquakes and tremors felt in Nepal are a dramatic manifestation of the ongoing convergence between the two plates.
- Pakistan – This country has recorded some of the most catastrophic and devastating earthquakes in the world. Pakistan lies in a region where Arabian, Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates meet and interact at different moving rates.
- Ecuador – This Latin American country is vulnerable because of the Nazca plate.
- Bangladesh – Like its neighboring countries is also vulnerable because of its dense population
- Guatemala – In 1976 this country was hit by a devastating earthquake that killed 23,000 people. Earthquakes are common here as Guatemala lies in a major fault zone – the Motagua and Chixoy-Polochic, which forms the tectonic boundary between the Caribbean Plate and the North American Plate.
- Peru – Located on the seismic zone, Peru is prone to very large earthquakes. South America is one of the most seismically active areas of the world.
- USA – Earthquakes are common on the west coast, the western mountain range, the Midwest south of the Great Lakes, and Hawaii. San Francisco is often hit by earthquakes with the San Andreas Fault being one of the seven significant fault zones in the Bay Area.









