NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope snapped a photo of a stunning nebula that resembles a massive floating rose in space. The agency explained that the nebula's image was formed by the new star formations inside it.
The subject featured in Spitzer's photo has been identified as NGC 1333. According to NASA, this impressive cosmic structure is located about 1,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Perseus.
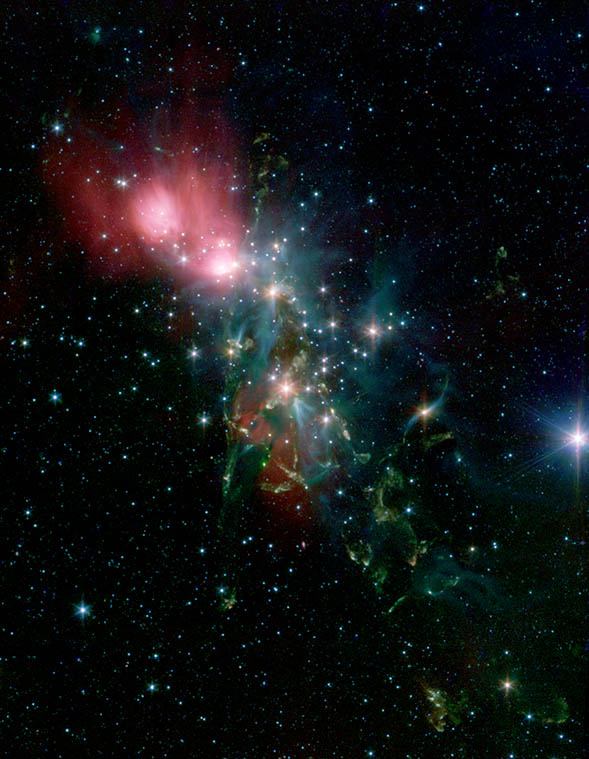
Shaping NGC 1333
As seen in Spitzer's photo, NGC 1333 looks like a giant flower red flower in space. NASA noted that its unique appearance was created by the different lights emitted by the stars and other cosmic materials inside the nebula. The reddish glow near the northern portion of the nebula was created by the infrared emissions of young stars. The southern portion of the nebula, on the other hand, features yellow and green coloured clouds.
"The knotty yellow-green features located in the lower portion of the image are glowing shock fronts where jets of material, spewed from extremely young embryonic stars, are ploughing into the cold, dense gas nearby," NASA explained in a statement. "In contrast, the upper portion of the image is dominated by the infrared light from warm dust, shown as red."

Newborn Stars In NGC 1333
The various infrared lights emitted by the nebula came from newborn stars. Unlike in other star-forming regions, the stars of NGC 1333 formed in different groups instead of clusters. Since they are in scattered groups, the nebula was able to take on a unique structure and overall shape. Normally, the infrared light emitted by the stars cannot be seen by the human eye. But, due to Spitzer's infrared imaging capabilities, the space telescope was able to photograph the nebula's colourful appearance.
According to NASA's observing and studying nebulas such as NGC 1333 provides valuable information regarding the formation of stars. They help scientists understand how the interaction between warm clouds and other cosmic materials can lead to the creation of stellar objects. The agency noted that this process is similar to the one stars like the Sun went through when they were forming.









