Researchers have potentially discovered the world's first cure for heart attacks by using mRNA technology which is used in Covid-19 vaccines.
Genetic tracking, which is followed in the Covid-19 vaccines, is now being adopted to help regenerate hearts damaged from cardiac arrests. The technology is used to make Moderna and Pfizer vaccines.
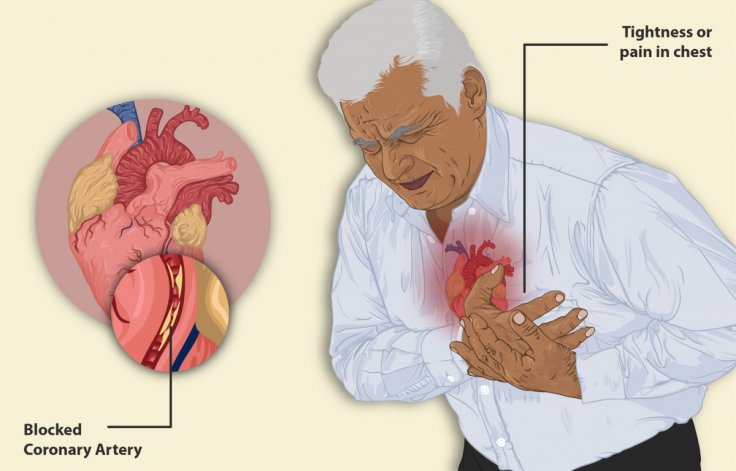
The ground-breaking heart attack cure has bee discovered at the King's College London.
Researchers Tracked Genetic Codes
Researchers have tracked genetic codes that are called mRNAs which produce proteins to generate healthy heart cells. The research is believed to lead to the world's first cure for heart attack victims, according to the Dailly Mail.
Lead researcher Professor Mauro Giacca revealed that all people are born with a set number of muscle cells in their hearts and they are exactly the same ones they will die with. "The heart has no capacity to repair itself after a heart attack. Our goal has been to find a treatment that can convince surviving cells to proliferate."
A few years ago, regeneration of a damaged human heart was impossible but it can become a reality now.
Pfizer, Moderna Vaccines' Technology
Researchers are using the same technology that Pfizer and Moderna vaccines use to inject micro RNAs to the heart, reaching surviving heart cells and pushing their proliferation. The new cells would replace the dead ones and instead of forming a scar, the patient has new muscle tissue.
Giacca's team is based at the British Heart Foundation Centre for Research Excellence at King's College London.
The research team, which is based at the British Heart Foundation Centre for Research Excellence at King's College London, is also working towards a treatment to stop cells from dying during a heart attack.
Nearly 1,00,000 people are hospitalized in the UK each year after a heart attack, that is caused by a blocked blood supply to the heart.
Usually, 100 billion heart cells are killed during a severe trauma caused by cardiac arrest.
The human heart lacks the ability to heal itself, which left many cardiac arrest victims with debilitating scars that lead to further complications.
Researchers believe that the new RNA (ribonucleic acid) therapy could revolutionize cardiovascular medicine and stop millions of heart attacks from progressing toward heart failure.
Trials to regenerate hearts could take place in humans in the next two years as recent trials to regenerate damaged pig hearts were successful.









