A study conducted on the Great Red Spot on Jupiter clarified the status of the massive atmospheric storm. According to the authors of the study, the Great Red Spot is still active despite its shrinking appearance.
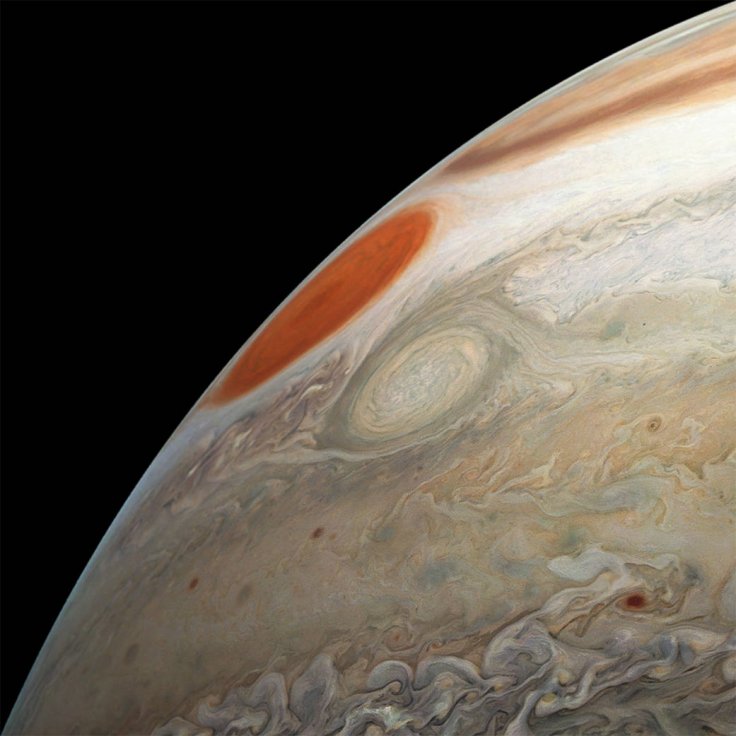
As revealed in scientific observations, the Great Red Spot on Jupiter is a high-pressure region on the planet's atmosphere. With wind speeds reaching up to 300 miles per hour, it is considered as the largest anticyclonic storm in the Solar System.
Jupiter's Shrinking Great Red Spot
Astronomers around the world have been observing the Great Red Spot on Jupiter for centuries. During the 1800s, early observations indicated that the massive storm was about three times the size of Earth. However, during the past decades, the diameter of the Great Red Spot has noticeably decreased. Today, Jupiter's prominent feature is only about as wide as Earth. Its shrinking size led to speculations that the Great Red Spot was nearing the end of its life cycle.
"In truth, the [Great Red Spot] has been shrinking for a long time," Glenn Orton, a planetary scientist and Juno mission team member at NASA told Business Insider. "The Great Red Spot will in a decade or two become the [Great Red Circle]. Maybe sometime after that the [Great Red Memory].
New Study On The Great Red Spot

Recently, a team of researchers released a new study claiming that the Great Red Spot is actually getting stronger. They made the conclusion after conducting an experiment using a Plexiglass tank filled with saltwater. Through the experiment, the researchers were able to simulate the conditions of large Jupiter vortices and how they evolve over time. The results from their experiment matched the measurements made by NASA's Voyager mission in 1979.
"For the Great Red Spot in particular, our predicted horizontal dimensions agree well with measurements at the cloud level since the Voyager mission in 1979," the researchers wrote in their study, which was published in the journal Nature.
Great Red Spot's Current Status
Through the experiment and other observations, the researchers learned that even though the diameter of the Great Red Spot has been shrinking for the past couple of decades and centuries, its overall thickness hasn't changed. The researchers estimated that the massive storm could be about 105 miles thick.
For the researchers, their findings support the idea that the vortex powering the storm is still very active. It is possible that it has maintained its strength, or it is still getting stronger.









