Omicron, the new variant of Covid-19 which has set alarm bells ringing across the globe, has more than double mutations as compared to Delta variant of the pandemic. The first image of the new variant, first detected in South Africa, was produced and published by researchers at the Bambino Gesu hospital in Rome.
The B. 1.1.529 variant, also known as Omicron, was first detected in South Africa and Botswana. Concerns are being raised as 24 percent of the population in South Africa is fully vaccinated.
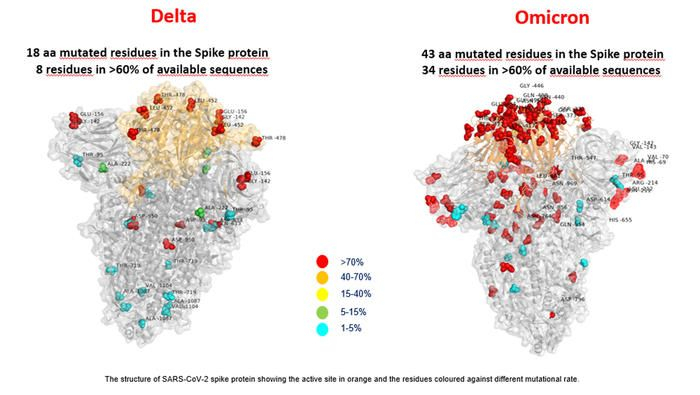
Mutations Concentrated in One Area of the Protein
The three-dimensional image of the new variant looks like a map. In a statement issued on Sunday, the team of researchers said that the virus had adapted to the human species by generating another variant. "We can clearly see that the Omicron variant presents many more mutations than the Delta variant, concentrated above all in one area of the protein that interacts with human cells", the statement read.
"This does not automatically mean that these variations are more dangerous, just that the virus has further adapted to the human species by generating another variant. Other studies will tell us if this adaptation is neutral, less dangerous or more dangerous," the team added.
Speaking to AFP, Claudia Alteri, professor of clinical microbiology at Milan State University and a researcher at Bambino Gesu said that while developing the image of Omicron, the research team focused on the search for mutations in "the three-dimensional structure of the spike protein."
The researcher also revealed that the Omicron's image was produced "from the study of the sequences of this new variant made available to the scientific community" coming mainly "from Botswana, South Africa and Hong Kong".
"This image, which represents a map of all the variations, describes the mutations of Omicron but does not define its role. It will now be important to define through laboratory experiments whether the combination of these mutations can have an impact on transmission or on the effectiveness of vaccines, for example," she added.
Omicron Has Higher Mutations Than Delta Variant
Speaking to News.com.au, Catherine Bennett, an epidemiologist Professor at the Deakin University, said that Omicron is different due to the high number of mutations it contains. Calling it unusual, the professor said, "In comparison to the handful of major mutations in other variants, the latest version had more than 50 mutations. More than 30 are in the spike region alone."
Earlier World Health Organization, who dubbed Omicron as Variant of Concern, said that the latest variant has at least 10 mutations linked to the receptor-binding domain on the protein spike.
"The concern is that when you have so many mutations, it can have an impact on how the virus behaves. It will take a few weeks for us to understand what impact this variant has on any potential vaccines," World Health Organisation technical lead on Covid-19, Maria Van Kerkhove had said.









