Researchers from Rice University, Houston, have developed a new mechanism that allows the editing of multiple DNA sites all at once, with the help of CRISPR/Cas9 technology. This new mechanism, referred to as the 'drive-and-process' or DAP is complicated but at the same time an exceptional innovation.
Initially the team of researchers speculated that multiple target base-pair editing with CRISPR-Cas12 might be an appropriate approach, but the end results were not satisfactory. This prompted them to consider the Cas9 technology, as per BioSpace.com
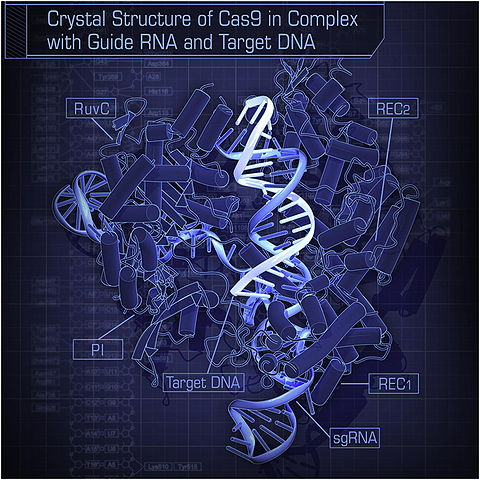
The researchers explained that the CRISP Cas9 technology utilizes the Cas9 protein, that is utilized in tracking down the DNA region with the help of a CRISP/Cas9 complex. Experiments were conducted via mammalian cell models to check whether diseases like muscular dystrophy, sickle cell or beta-thalassemia could be suppressed with the new DAP mechanism.

With successful results the researchers were able to deduce that the DAP is not only compatible with viral vectors but also does not affect any unintended genetic targets.
The study's lead author, Qichen Yuan of Rice's George R. Brown School of Engineering, commented, "previously, if we wanted to edit multiple genes in the same cell, we would have to do them one after another, which is very time-consuming and low-efficiency."
"Now, we have a much neater solution. For this paper, we demonstrated 31, but in principle with a single DAP array, if not limited by manufacturing and delivery, we could achieve as many edits as we want," he added further. The experimentation proved that almost 31 genetic sites could be altered with the new mechanism.
The researchers believe that the DAP technology is a much needed improvement that could finally provide a solution to the numerous problems encountered while treating polygenic diseases.
The fast-paced evolution of research technology which led to the disclosure of the central mechanisms of various diseases has revealed that in most cases there are multiple contributing factors, the DAP mechanism can therefore be utilized for a better diagnosis and treatment of such diseases.









