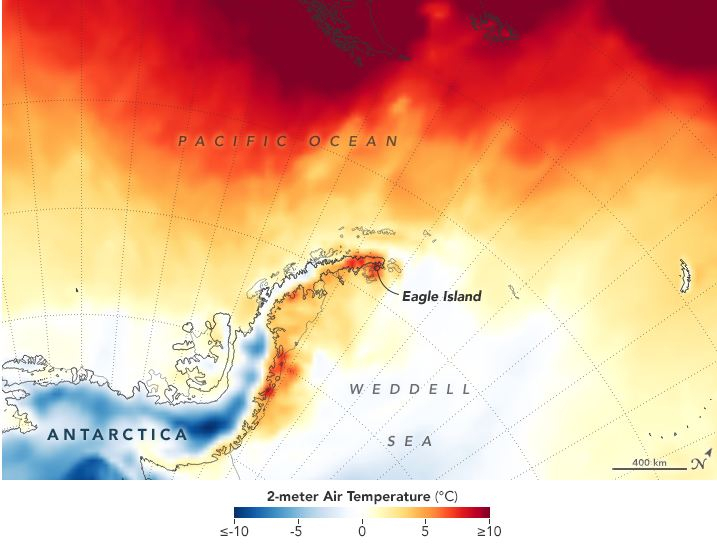
The US space agency NASA has captured the images of Antarctica and showed a new side of the location which is now completely ice-free. Even though these images are essentially beautiful, the current scenario at Antarctica's Eagle Island is posing threat to the world oceans and making the scientists more worried than ever.
Just a few days ago Antarctica has recorded nearly 64.9 degrees Fahrenheit, which is a new temperature record on the continent and scientists mentioned that they are currently worried about the speedy collapse of two most vulnerable glaciers, which are Pine Island Glacier and Thwaites 'Doomsday' Glacier.
Eagle Island
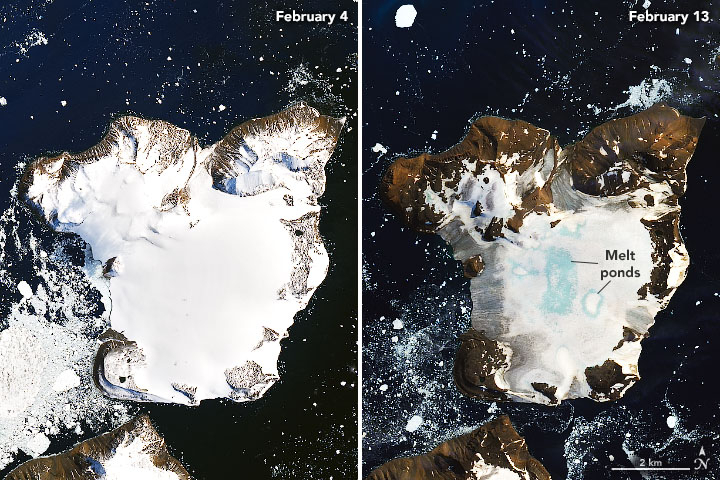
As per these newly released before and after images by NASA, 20 percent of the snow on one ice cap in Antarctica melted in the heatwave between February 4 and 13. According to environmentalists, these images revealed that the Eagle Island, one of the several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land that is closer to South America, was nearly covered in snow on February 4 but by February 13 most of the snow has melted, revealing large amounts of the landmass.
The second image showed a few light blue portions, which are the areas that have now turned into ponds due to the snowpack being saturated with water caused by the melting and these pond-like areas soak up heat more than snow which can accelerate the melting process.

Antarctica under threat
Mauri Pelto, a glaciologist at Nichols College stated, "I haven't seen melt ponds develop this quickly in Antarctica. You see these kinds of melt events in Alaska and Greenland, but not usually in Antarctica." He mentioned that since warm temperatures are happening more and more often in the region, the melt events can soon change. The National Snow and Ice Data Center have shown that some parts of the area have warmed up over four and a half degrees Fahrenheit since '50s.
In relation to these climate change-related issued, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk talked about those human actions that can accelerate the transition out of the fossil fuel era. In his speech at the Sorbonne in Paris, right before the historic COP21 climate change conference, Musk said "This temperature increase, people talk two degrees or three degrees — it's important to appreciate just how sensitive the climate actually is to temperature."
He explained that it's "important to look at it in terms of absolute temperature, not in degrees Celsius relative to zero. We need to say, what the temperature change relative to absolute zero is. That's how the universe thinks about temperature. That's how physics thinks about temperature. It's relative to absolute zero. So, small changes result in huge effects."
While giving an example the technology entrepreneur showed visuals, particularly for those people who don't understand terms such as absolute zero or how it would affect our day to day life. He mentioned that "New York City under ice would be minus 5 degrees. New York City underwater would be plus 5 degrees. But looked at as a percentage relative to absolute zero, it's only a plus/minus 2 percent change. The sensitivity of the climate is extremely, extremely high. We've amplified this sensitivity by building our cities right on the coastline and most people live very close to the ocean."
Why it is relevant to Antarctica
The discussions and examples Musk put forward during his speech can be applied to the threatening case of Antarctica, as it showed that over four degrees of change can have a huge impact on the climate. In this case, Pelto gives a warning stating what humans can expect. He revealed that "If you think about this one event in February, it isn't that significant. It's more significant that these events are coming more frequently."
Alexandra Isern, head of Antarctic sciences at the National Science Foundation also revealed that these warm events in the part of the peninsula are occurring more frequently. While discussing the new images, she also cautioned: "We have to understand that those images were taken about as far north in Antarctica as you can get. So if any place is going to have those melt ponds, that's certainly going to be one place."









