Satellite data has revealed that an ice shelf nearly the size of Rome has collapsed in Antarctica as the region recorded the highest temperature in recent days. The Conger ice shelf, which has an approximate surface area of 1,200 sq km, collapsed in East Antarctica around March 15.
Last week, the region witnessed high temperatures with Concordia station hitting a record temperature of -11.8C on March 18, more than 40C warmer than seasonal norms. The high temperature was believed to be the result of an atmospheric river that trapped heat over the continent, according to The Guardian.

How Did The Conger Ice Shelf Collapse?
Extensions of ice sheets are ice shelves that float over the ocean and play e key role in restraining inland ice. In the absence of ice sheets, inland ice flows faster into the ocean, which results in the sea level rise.
Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission's satellite data has revealed that movement on the ice shelf appeared to show around on March 5.
The collapse of the Conger ice shelf is considered to be a major event in Antarctica since the early 2000s when another ice shelf Larsen B disintegrated. Scientists have cleared that it would not make any record-breaking change but the incident is a warning of possible future events.
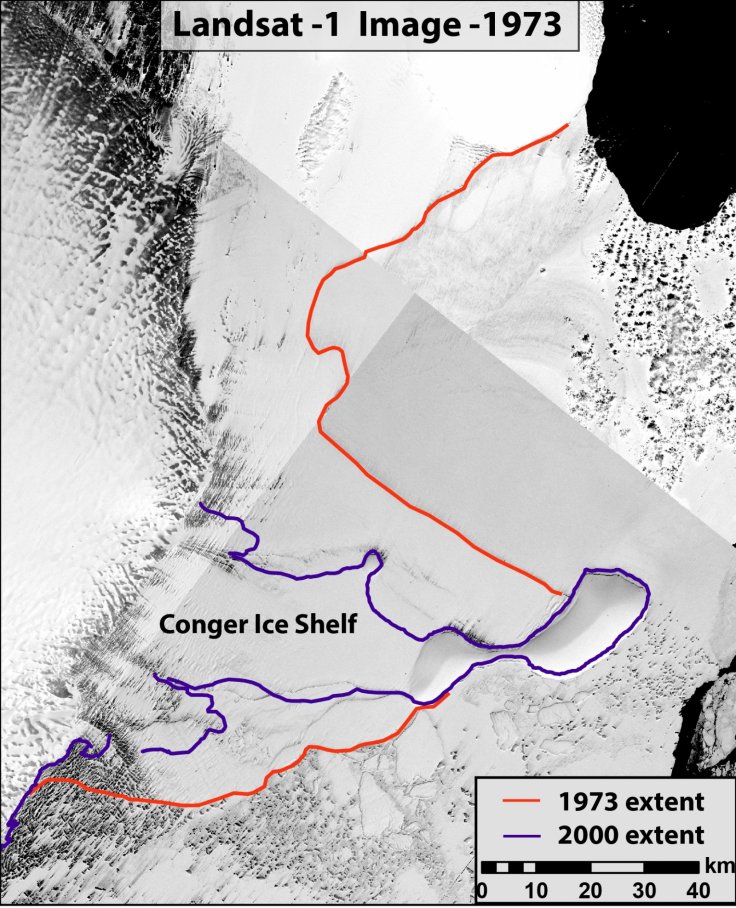
The Conger ice shelf started shrinking slowly since the early 2000s but after 2020 its shrinking turned a bit quicker. The ice shelf has lost more than half of its surface area by March 4 When compared to January measurements of around 1,200 sq km.
Scientists have maintained that even a small ice shelf collapse in East Antarctica is a surprise and it shows climate change in a rapid way.
Doomsday Glacier
Concerns are also rising about the future of the Thwaites glacier, a Florida-sized glacier, which is nearly 100 times larger than Larsen B. The glacier possibly contains enough water to raise sea levels worldwide by over half a meter.
Scientists have analyzed the speed of the break of ice shelves can change quickly as the collapse of the Conger ice shelf has shown. They have warned that the global carbon emissions have shown their impact on Antarctica and will hamper the world's coastlines in a faster way than considered.








